Taxpayers filing their return using ITR Form-1 (Sahaj) can find all the information in their Form-16. Form-16 provides all the information about their salary details which includes basic, allowances, perquisites etc.
While Form16 provides you all the details regarding your salary income, here's how you must fill the required details to file your return correctly. Incorrect details could lead to scrutiny from income tax department.
Income from salary
Under this head in ITR Form-1, you are required to enter the following details related to salary: Salary (excluding all allowances, perquisites and profit in lieu of salary), allowances that are not exempt from tax, value of perquisites, and profit in lieu of salary. You will also have to provide details of the deductions you have claimed under section 16 of the Income-tax Act, 1961.
Here is how each of these heads will be taxed:
Salary (excluding all allowances, perquisites, profit in lieu of salary)
Here, the taxpayer is required to input the details of salary, i.e., basic salary. This part of your in-hand salary is fully taxable.
Allowances not exempt from tax
While it is a well-known fact that the basic salary is fully taxable, not all allowances that are part of your in-hand salary are fully taxable. Some of them are tax exempt up to a certain amount, whereas some are fully taxable.
Transport allowance for and up to FY 2017-18 is exempt from tax up to Rs 1,600 per month or Rs 19,200 annually. Any amount received over and above that will be chargeable to tax. Similarly, a certain part of house rent allowance (HRA) is taxed depending on the actual amount received by you and certain other conditions.
Click here to calculate how much HRA will be tax exempt.
On the other hand, special allowance received is fully taxable in your hands. Leave travel allowance (LTA) is exempted from tax based on certain parameters. Click here to read more about tax exemption limits of various allowances.
Also Read:
How to fill salary details in ITR-1 for FY 2017-18
ITR Form-1 for FY 2016-17/ AY 2017-18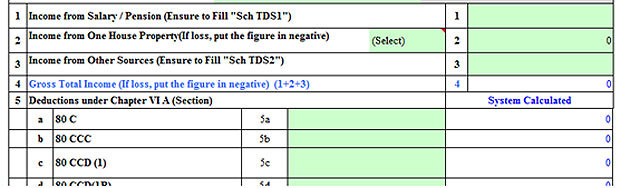
(Snapshot of ITR Form-1 in excel utility)
ITR Form-1 for FY 2017-18/ AY 2018-19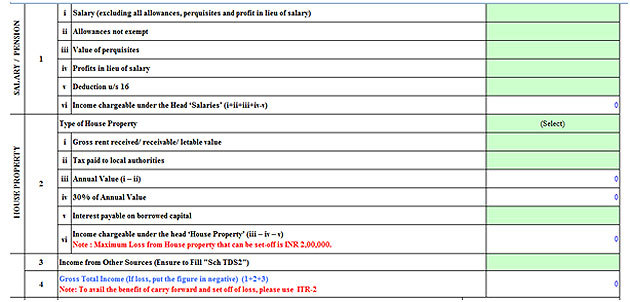
(Snapshot from ITR Form-1 in excel utility)
Perquisites
Perquisites refer to a benefit that employees enjoy or are entitled to on account of their job or position. Income tax laws define perquisites as any casual emolument or benefit attached to an office or position in addition to salary or wages.
According to section 17(2) of the Income-tax Act, perquisites include:
a) Rent-free or concessional rent accommodation provided by the employer.
b) Any sum paid by the employer on behalf of an employee because of employee's obligation like life insurance premium;
c) Any benefit granted free or at a concessional rate to an employee;
d) Any specified security or sweat equity shares allotted or transferred, directly or indirectly by the employer or former employer free of cost or at a concessional rate;
e) Any contributory amount to an approved superannuation fund by the employer on behalf of employee, that exceeds Rs 1.5 lakh; and
f) Value of any other fringe benefit or amenity such as interest free or concessional loans etc.
The value of these perquisites are calculated by your employer and is added to your salary package. However, not all the perquisites are fully taxable at their cost and some of them are even exempt from tax. Valuation of the above mentioned perquisites are done based on the rules governing the same to determine their cost. This cost is then added to your salary and taxed at the rates applicable to your income
For instance, if you are living on a rent-free accommodation, owned by your employer, then the value of this accommodation will be calculated as follows: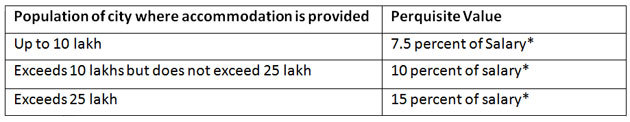
Source: Taxmann.com
*Here salary includes basic, dearness allowances if any, all taxable allowances, bonus, commission. On the other hand, if the house is taken on rent by your employer, then cost is calculated as: Lease rent paid or payable by the employer or 15 percent of the salary, whichever is lower.
Similarly, the cost of employees' stock options (ESOPs) or sweat equity shares issued will be calculated as: Fair market value of shares or securities on date of exercising option by the employee minus amount paid by employee.
Interest that would have normally been payable on interest free or concessional loans of up to Rs 20,000 or loans made for medical treatment of specified diseases such as cancer, TB etc., are not chargeable to tax as a perquisite. Expenses in relation to telephone or mobile phones, providing laptop for work purposes are not treated as a perquisite, if used for official purposes.
Any gift or voucher received by an employee on ceremonial occasions or otherwise is regarded as a perquisite. These gifts are taxable fully if received in cash or exempt up to Rs 5,000 if received in kind such as gift cards, adds Mittal. Therefore, if you have received a gift card of Rs 20,000 from your employer, then only Rs 5,000 will be exempt from tax. The balance of Rs 15,000 will be added to your salary and taxed accordingly.
Profit in lieu of salary
Section 17 of the income tax Act states that any payment received by an employee in addition to salary or wages will be charged as 'Profit in lieu of salary'.
This type of payment usually includes retrenchment benefit, interest received from your exempted recognised provident fund in excess of 9.5 per cent per annum or payment received by the employee before joining or after the termination of employment. Taxes levied on these payments are same as chargeable to your income as per the slabs.
Deductions under section 16
This section pertains to the deductions that you can claim from your salary income only. Following are the list of deductions under section 16 that can be claimed for FY 2017-18:
a) Deduction on entertainment allowance received by government employees only which is lower of:
i) Actual amount received
ii) One-fifth of the salary excluding any allowance, benefit or other perquisite
iii) Rs 5,000
b) Any professional or employment tax paid
Standard deduction of Rs 40,000 introduced in the budget 2018 will be available to taxpayers from the next year, i.e., FY 2019-20 onwards.
Income from house property
Apart from providing salary break up, taxpayers who have one house property are also required to provide details about the same. In last year's form, taxpayers had to only mention the amount of income earned from the house property without providing any extra details of the same.
Taxpayers are will now have to provide details such as whether the house property is self-occupied or let out, gross rent received or receivable, taxes paid you, interest payments on home loan, annual value of the house and so on.
Type of house
While filing ITR, one has to select whether the house is 'self-occupied' or 'let out'. Taxability of income from house property depends whether the said house is self-occupied by the taxpayer or let out.
If the house property is neither let out nor self-occupied, then also the income from it is still chargeable to tax and the taxpayer is required to pay tax on the deemed rent, i.e., rent he/she would actually earn if the property would have been let out.
In case of let out property
If the house is let out, then value is calculated on the gross rent received less of taxes paid to the municipal corporation, i.e., property tax or house tax.
Gross Rent Received/Receivable/Letable Value: A taxpayer has to mention the amount that is actually received by them as rent during FY 2017-18 from letting out the property.
In case of deemed rent, one is required to take highest of: a) Rent received or receivable, b) Fair Market Value and c) Municipal valuation to arrive at lettable value.
Taxes paid: Property tax or house tax is the tax which is actually paid to the municipal corporation on the rented property.
Annual Value: The value arrived at by deducting taxes paid from gross rent received is called Annual Value.
From this annual value, a taxpayer can claim two deductions under section 24: a) deduction of 30 percent from annual value and b) interest payments made on home loan.
30 percent of annual value: It is a deduction allowed as 30 per cent of the annual value. It is irrespective of the amount spent on maintenance, electricity bills etc.
Interest payable on borrowed capital: If interest payments on home loan have been made in FY 2017-18, then one can claim deductions on that too.
Self-occupied property
On the other hand, if house is self-occupied by the taxpayer, then annual value is considered as zero. Here a taxpayer can claim only deduction on interest payments made on the home loan.
The maximum deduction on such an interest payment is allowed up to Rs 2 lakh for both, self occupied and let out properties.
Income chargeable from house property: The result you will get from making the above calculations (depending on type of house property) will be chargeable to tax.
SIPs are Best Investments as Stock Market s are move up and down. Volatile is your best friend in making Money and creating enormous Wealth, If you have patience and long term Investing orientation. Invest in Best SIP Mutual Funds and get good returns over a period of time. Know which are the Top SIP Funds to Invest Save Tax Get Rich - Best ELSS Funds
For more information on Top SIP Mutual Funds contact Save Tax Get Rich on 94 8300 8300
OR
You can write to us at
Invest [at] SaveTaxGetRich [dot] Com